Required Items
- Laptop with CyberPower PowerPanel Personal Installed
- Click here for installation link
- Ethernet Cable
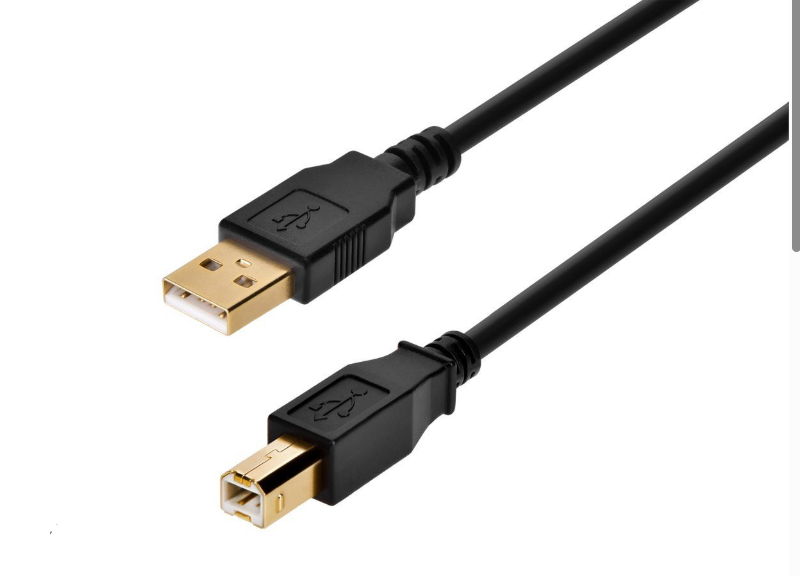
- USB A to USB B cable (image below)

Instructions
- Upon locating UPS (and if necessary installing PowerPlan Personal), open PowerPlan Personal and follow the checklist below.
- Open PowerPlan Personal
- You will be directed to a home screen that provides the current status of the UPS.
- At the top are four pages that you may click on. They are a house, file, a settings cog, and an info page. Click on the settings cog.
- Below the settings cog more options will appear. Click on notification, and scroll to the bottom of the page.
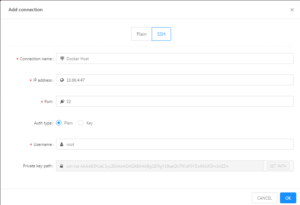
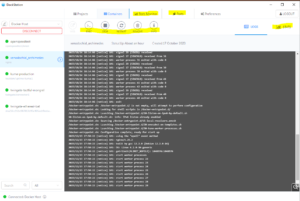
- This page is where the email can be configured. All configurations should be filled in, however, if they are not please reference image 2. The only thing you will need to change in this process is the sender name.
- Set the laptop in a safe place and move on to step two. We will come back to the laptop later.
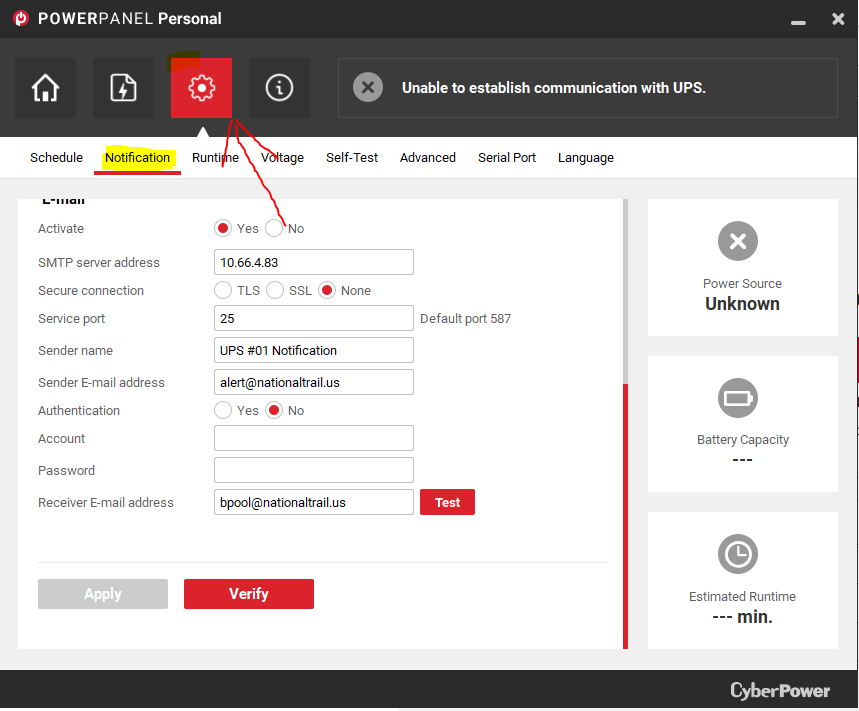
NOTE: The settings in the image above must be set as shown. If they are not, update them to match this image. The only thing that will be edited after the fact will be the sender name.
- Locate the top switch
- The top switch should always be located at the top of switches in the server rack, however it is good practice to use the following checklists to verify.
- Checklist 1:
- It is likely that the switches will be labeled with numbers. Check the front panel of the switch for this number and locate switch one. Switch one will always be the top switch.
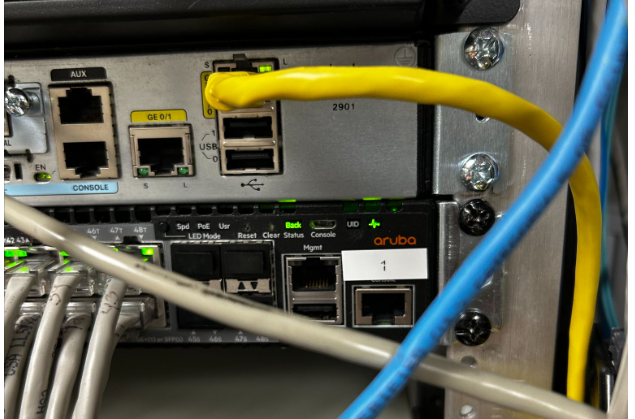

- Checklist 2:
- If the switch is not labeled you will need to locate the top switch via the switch stacking cables. The top switch will be at the top of these.
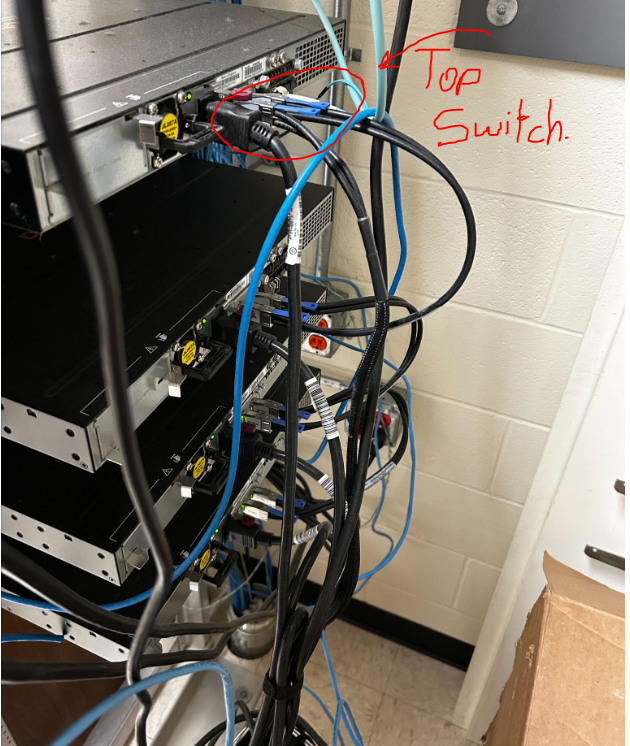

- Some racks of camera switches in addition to communication switches, for instance, the maintenance closet which has camera switches as well. In this case, you will need to differentiate between the switches that connect to the cameras and the switches that do not. These switches will be labeled, and if they are not, check that they are connected via ethernet cables.
- Checklist 1:
- The top switch should always be located at the top of switches in the server rack, however it is good practice to use the following checklists to verify.
- Plug in ethernet cable to switch and UPS
- The UPS will have an ethernet port labeled, “in”. Plug the first end of ethernet cable into this port.

- Using the most direct and least obstructive path, plug in the second end of the ethernet cable into the switch. It is absolutely crucial that you do not obstruct the front of a different UPS or run a cable through a slot that a UPS/Switch could fit into.
- If at all possible, DO NOT, run the cable through existing ethernet cables, but rather run the cable behind them to avoid tangling.
- Final Step: Using PowerPlan Personal
- With the ethernet cables plugged in and PowerPlan Personal opened and properly setup, plug in the USB A to USB B cable into the laptop and the correct UPS port, likely titled communication port. (image below)

- Next, change the number in the sender name. If it is a single digit, add a 0 in front of the number.
- Ex. UPS #11 Notification —> UPS #09 Notification
- Lastly, click “Apply”. If it applies successfully, move onto the next step.
- Click “Verify”. If it verifies successfully, move onto the next step.
- Finally, click “Test”. If it tests successfully, you have finished and may unplug the laptop from the UPS.